The NDIS includes support and funding for many individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). However, navigating the complexities of the NDIS funding, applying, and getting your application approved, can seem a more tedious process than expected. While the NDIS covers Autism, it is crucial to ensure eligibility for the scheme.
There are different degrees of ASD that impact the level of support you receive from NDIS. If an individual has a Level 2 or Level 3 ASD diagnosis, they are eligible for the NDIS support. However, in the case of Level 1 ASD diagnosis, the individual must provide additional details regarding the disability. It includes the impact of your disability on your everyday life across various factors – communication, social interaction, mobility, self-management, and self-care.
Every individual with ASD is different, and we can’t fit all of them in one distinct category. Many autistic individuals require more support than others in specific areas. The good news is that NDIS depends on evidence for its final decisions. Hence, the more evidence you have that shows you need support in one area or more, the more likely is NDIS to approve your application.
What is Autism?
Autism or Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a developmental disability that can affect an individual’s ability to interact socially and other behaviours. It is a common disability that affects 1% of the population.
While Autism can refer to a specific disability, ASD covers a range of developmental disorders such as Autism, Asperger syndrome, and pervasive developmental disorder (PDD-NOS). The disability is on a spectrum which indicates that no two people with ASD are alike with the same needs. The characteristics and severity of the disability can vary in every person. However, some signs are common, including the following behaviours –
- Delayed or abnormal behaviour and language patterns
- Repetitive, obsessive, restricted, and/or isolated behaviour
- Impulsive body movements that can lead to self-injury – flapping, toe walking etc.
- Dedicated to rigid rituals and routines – disruptions can cause high levels of stress
- Obsessive tantrums can lead to frustration, confusion, stress, and anger
- Sensory issues – increased sensitivity towards specific stimuli such as sounds, taste, textures, and smell.
Common signs and symptoms also include speech, sleep, and language difficulties, depression, anxiety, poor motor skills, epilepsy, etc.
Many individuals with ASD can show high levels of sensitivity towards taste, sound, smell, touch, and vision. The sensitivity can result in strong reactions and outbursts that can generate distress for individuals with ASD and their family members.
Severity of ASD
Autism is a spectrum disorder. It indicates varying levels of severity. Hence, an individual with ASD can be mildly, moderately, and severely autistic – indicating varying needs.
When a doctor diagnoses an individual with ASD, they must assign a level. The three levels reflect the different abilities of the individual – communication, daily tasks, adaption to change, and willingness to expand beyond their restricted interests. Here’s a breakdown –
Level 1 Autism
Individuals require a mild level of support, usually with social interactions and organisational and planning abilities. Capacity building supports can aid in developing skills that can help them lead an independent life.
Level 2 Autism
Individuals require substantial support regarding their limited social interaction with specific interests and other restricted/repetitive/obsessive behaviours.
Level 3 Autism
Participants require very substantial support due to severe deficits in social communications and other difficulties in changing focus and/or actions.
What will the NDIS funding include for individuals with Autism?
The NDIS funding covers various supports dependent on the individual’s situation. The NDIA will create a unique NDIS plan for each participant that accommodates their situation. It will cover the condition of their disability, the support they need, and the funding they require. Each NDIS plan is different based on different support needs & goals. It depends on what the participants want to achieve from the NDIS plan.
The goals can involve –
- Physical aspects – Participants wish to walk without any assistance
- Social aspects – Participants want to be involved in the community and make new friends
- Independence – Building confidence, ability to carry out regular tasks alone, travel alone, etc.
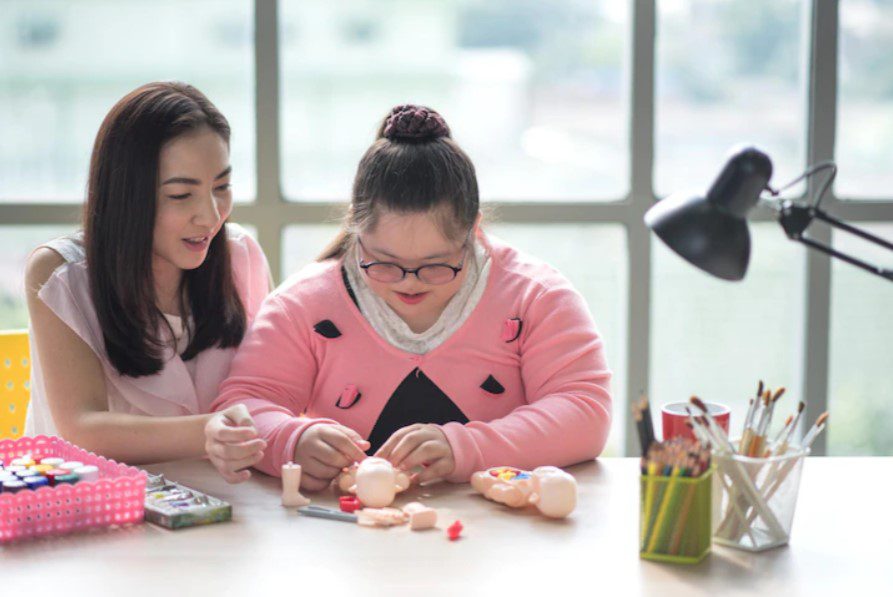

However, it is crucial to discuss your goals during your planning meeting so the support coordinator can design your plan accordingly and ensure you get the funding you need. Despite unique needs, here are the common NDIS supports included in ASD related plans –
- Physiotherapy – to develop motor skills
- Speech therapy – to help communication skills
- Holiday camps – to boost social and interpersonal skills
- Sensory toys – to help act as therapeutic aids
- Support worker – to assist the individual at home
If you’re new to NDIS and are looking through different supports, you’re likely to come across the term – reasonable and necessary. It means that the NDIS plan will only support and fund things necessary for your disability with the right value for money.
NDIS Support Categories
NDIS funding includes three different kinds of support categories – Core, Capital, and Capacity Building.
Core supports, as the name suggests, help with essential, day to day activities that can be impacted by your disability. It helps with daily activities, social participation, transport, and other everyday items you may need. Core supports provide the funding and support to help resume the daily activities in your life.
Capacity building supports aim to increase your independence and help achieve your goals. Unlike Core supports funding, your budget can’t be transferred to another support category. Capacity-building support helps in multiple aspects –
Support coordination, improvement in current living arrangements, better social participation, a job with relevant skills, learning and educational opportunities, etc.
In short, it helps build skills and find jobs to help you lead an independent life.
Capital supports focus on technology – any equipment, vehicular or home modification. Capital supports also can’t be transferred to another support category and can only be used on assistive technology or home modifications. It includes equipment items – wheelchairs – or installations – handrails in bathrooms.
NDIS for Children – Early Childhood Approach
CHILDREN OVER 7 YEARS
If your child is diagnosed with ASD and is over seven years of age, they can apply for the NDIS plan via the NDIS pathway. If you need an overview of the NDIS process – how to apply, eligibility criteria, planning meeting, requesting a review – click here.
CHILDREN OF AGES 0-6 YEARS
If your child is diagnosed with ASD and aged 0-6 years, they can apply for the NDIS plan via the Early Childhood Approach. This approach aims to provide the right support at the right time, with timely access. Moreover, it provides information regarding the best practices of early childhood intervention that can help support your child. The plan also improves confidence and focuses on capacity building exercises while responding to your child’s unique needs (related to their disability).
The NDIS support encourages your children to perform their daily activities independently and participate in the community – recreation, child care, friendships, etc. Moreover, if needed, the NDIS plan also covers any information or referrals needed, such as parent support groups. Living with a disability can be difficult, and the NDIS ensures that the individual isn’t dependent on the support long term. The early intervention aims to reduce the impact of the disability and help the child lead an independent life.
NDIS eligibility based on ASD Diagnosis
According to the latest version of the DSM-5 (Diagnostic and Statistical Manual), ASD divides into three distinct categories – Level 1, Level 2, and Level 3
While all three categories require support, Level 1 requires the least support, while Level 3 demands substantial support. The NDIS eligibility depends upon the functional capacity of the individual and how the disability impacts their capacity. It includes areas of communication, social interaction, mobility, self-care, and self-management.
Seek help from a United Legal Lawyer today
If you’re trying to apply for the NDIS plan, it’s always best to contact an experienced lawyer to help navigate the process. Many people with disabilities have claimed that the NDIS appeals can be ” soul-destroying ” as an alarming number of individuals walk through the process without legal representation.
It’s crucial to prepare for the NDIS plan, so we outline the different stages of the journey you’re about to start so you get the maximum support you deserve. The planning meeting is the most important step that decides the result of your application, your support & funding, and other related aspects of your NDIS plan. Hence, it is crucial that you are well aware of the elements you want to discuss and address, clearly describing your goals. Moreover, we ensure that you have the right documentation to support your case while preparing you for the questions your coordinator may ask.
Living with a disability has its challenges. Hence, United Legal takes over the responsibility of the tedious NDIS application, so you can focus on getting the most out of the situation and your NDIS plan. We cover every aspect to ensure you have a strong case and that your NDIS funding aligns with your goals. Take the step today and contact us for further details.
For our legal support services, contact us at (02) 6295 228
United Legal
Canberra Public Liability Lawyers
Visit us at
54-56 Townsville St, Fyshwick ACT 2609